As global industries face increasing pressure to reduce emissions and operate responsibly, packaging has emerged as a surprisingly powerful lever for change. Packaging is no longer just about protecting goods in transit; it has become a strategic component of sustainability planning. From raw material extraction to disposal, traditional single-use returnable packaging solutions contributes significantly to landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
In this context, Returnable Packaging Solutions are gaining traction as an effective and practical way to reduce carbon footprints while also improving operational efficiency. These systems are reshaping how companies think about logistics, waste, and long-term value creation.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Carbon Footprint of Conventional Packaging
To appreciate the benefits of returnable systems, it’s important to understand the environmental cost of conventional packaging. Single-use pallets, cardboard boxes, shrink wrap, and plastic containers often have short lifespans. After one or two trips, they are discarded, recycled with energy-intensive processes, or sent to landfills.
Each stage of this lifecycle adds emissions:
- Raw material extraction consumes natural resources and energy
- Manufacturing releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants
- Transportation increases fuel consumption due to constant replacement
- Disposal or recycling requires additional energy and infrastructure
When scaled across global supply chains, these impacts become substantial. Reducing this cycle is key to lowering overall emissions.
What Are Returnable Packaging Systems?
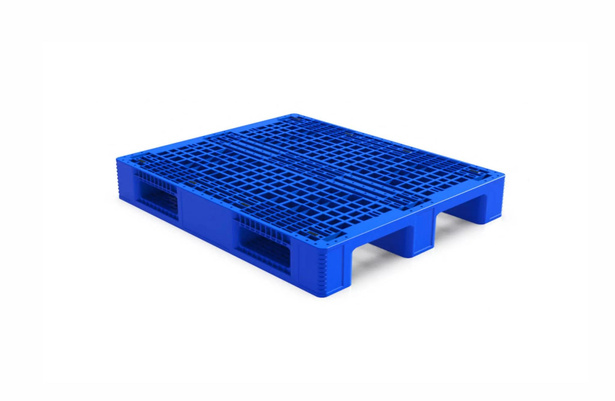
Returnable packaging systems are designed for repeated use across multiple supply chain cycles. Instead of being discarded after delivery, packaging components are collected, inspected, cleaned if necessary, and reintroduced into circulation. Common examples include reusable pallets, containers, crates, and dunnage.
These systems are typically built from durable materials such as high-density plastics or engineered composites, allowing them to withstand repeated handling without compromising performance. The result is packaging that behaves more like an asset than a consumable expense.
How Reusability Drives Carbon Reduction
The environmental advantage of returnable systems lies primarily in their ability to eliminate repeated production. A single reusable pallet can replace dozens of disposable alternatives over its lifetime. This reduction in manufacturing demand directly translates to lower emissions.
Additionally, optimized designs often weigh less than traditional wooden pallets, which reduces fuel consumption during transportation. Fewer replacements also mean fewer trucks hauling packaging materials to manufacturing and disposal facilities.
Over time, the cumulative effect is a measurable decrease in a company’s carbon footprint, particularly in industries with high shipment volumes.
Lifecycle Assessment: A Clear Sustainability Advantage
Lifecycle assessments (LCAs) consistently show that reusable packaging outperforms single-use options when used at scale. While the initial manufacturing footprint of a reusable item may be higher, this impact is quickly offset after multiple trips.
For example, a reusable pallet that completes 50 to 100 trips dramatically lowers emissions per use compared to a wooden pallet used once or twice. This “break-even” point is often reached much sooner than companies expect, especially in closed-loop or regional supply chains.
Operational Efficiency and Environmental Gains
Sustainability and efficiency often go hand in hand. Reusable packaging systems are typically standardized, which simplifies stacking, storage, and transportation. This uniformity allows for better space utilization in warehouses and trucks, reducing the number of trips required.
Less damage during transit is another key benefit. Durable packaging protects goods more effectively, reducing product loss and the emissions associated with replacements and returns. In this way, carbon reduction is achieved not only through packaging itself but also through improved overall logistics performance.
Waste Reduction and Circular Economy Alignment
One of the most visible benefits of reusable packaging is waste reduction. By keeping materials in circulation, companies move closer to a circular economy model where resources are reused rather than discarded.
This approach reduces landfill dependency and lowers the environmental burden on local waste management systems. It also aligns with increasingly strict environmental regulations and consumer expectations around responsible business practices.
Measuring and Reporting Sustainability Impact
Modern supply chains are increasingly data-driven, and reusable packaging systems fit well into this model. Many solutions integrate tracking technologies such as RFID or barcodes, enabling companies to monitor usage rates, loss, and environmental impact.
This data supports accurate sustainability reporting, helping organizations quantify carbon savings and demonstrate progress toward environmental goals. Transparent reporting not only builds trust with stakeholders but also strengthens brand reputation in competitive markets.
Industry Adoption and Future Trends
Across automotive, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and retail sectors, reusable packaging is becoming a standard rather than an exception. Companies are recognizing that sustainability initiatives must deliver real operational value to be successful.
As materials science advances and logistics networks become more connected, returnable systems will continue to evolve. Lighter designs, longer lifespans, and smarter tracking will further enhance their carbon reduction potential.
The Role of Collaboration in Success
Implementing reusable packaging is not a solo effort. It requires coordination between manufacturers, suppliers, logistics providers, and customers. When partners share responsibility for returns and maintenance, systems become more efficient and environmentally effective.
This collaborative approach fosters long-term relationships and shared sustainability goals, reinforcing the idea that carbon reduction is a collective responsibility rather than an isolated initiative.
Conclusion:-
Reducing carbon footprints doesn’t always require radical innovation; sometimes it means rethinking everyday processes. Returnable Packaging Solutions offer a proven, scalable way to cut emissions, reduce waste, and improve supply chain efficiency at the same time.
By treating packaging as a reusable asset instead of disposable waste, companies can make meaningful progress toward sustainability targets while strengthening their operations. As more organizations adopt these systems, partners like Kole Pallet play an important role in supporting the transition toward a cleaner, more efficient, and more responsible supply chain future.
Frequently Asked Questions:-
1. What are returnable packaging solutions, and how do they work?
- Returnable packaging solutions are reusable packaging systems designed to be used multiple times within a supply chain. After delivery, the packaging is collected, inspected, and reused instead of being discarded. This repeated use reduces waste, lowers production demand, and minimizes environmental impact.
2. How do returnable packaging systems help reduce carbon emissions?
- These systems reduce carbon emissions by eliminating the need for constant manufacturing of single-use packaging. Fewer raw materials, less energy consumption, and reduced transportation of replacement packaging all contribute to a lower overall carbon footprint.
3. Are returnable packaging solutions suitable for all industries?
- Yes, many industries can benefit from returnable packaging, including automotive, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, retail, and manufacturing. They are especially effective in high-volume or closed-loop supply chains where packaging can be easily returned and reused.
4. Is the initial investment in reusable packaging cost-effective?
- While the upfront cost may be higher than disposable packaging, returnable systems typically deliver long-term cost savings. Reduced replacement expenses, lower waste management costs, and improved logistics efficiency often result in a strong return on investment over time.
5. How do reusable packaging systems support sustainability goals?
- Reusable packaging supports sustainability by reducing landfill waste, conserving natural resources, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and aligning businesses with circular economy principles. These benefits also help companies meet regulatory requirements and strengthen their environmental credibility.